摘要: 2018年AP心理学考试真题及答案解析
上一篇小编给大家分享了2018年AP物理2真题解析高清扫描版免费下载(FR),今天上海新航道AP培训中心接着分享.2018年AP心理学考试真题及答案解析。需要报考2019年5月AP考试的同学,刚好用上!一起来看一下详细内容:
第一题

解析:
本题跟07、16年第1大题如出一辙,内容清晰明确,用Part A和Part B的Key
terms分别解释如何帮助或阻碍案例中Jackie的表现。
Proactive interference 在15,16年真题中原题出现,Yerkes–Dodson law of arousal与locus of control 在近10年真题中也多次出现类似表达,Ach属于Neurotransmitters 的重点,MCQ反复考察。Context-dependent Memory容易理解与记忆,但可能会与state-dependent memory搞混。
虽然很多考生都觉得Kinesthetic sense比较难,没见过,但如果认识单词,基本可以猜出章节(sensation and perception),它与vestibular sense都属于body position sense,前者也多次考过,所以这个terms看似较难,但比较容易解释,尤其对于细心或灵活思辨的学生易得分。
PART A
Point 1: Context-dependent memory
It is an effect of context on memory. Putting yourself back in the context where you experienced something can prime your memory retrieval. If Jackie acts the play on the same stage where she used to practice, it will help her performance better.
Teacher's feedback:
1.Context-dependent memory是依赖外部线索(身临其境)影响信息提取(recall)的一种效应,它本身不是一种记忆类型;
2.注意Context-dependent memory与State-dependent memory的区别:前者是相同环境下有助于回忆,后者相同状态下有助于回忆。前者是外部线索,后者是内部状态(情绪或醉酒等);
3.没有Mood-dependent memory这个terms,很多同学会搞混,只有mood congruent(心境一致性),记忆或多或少总是与心境保持一致的,所以当你在积极情绪下学习的东西,在相同积极情绪下更能有效回忆。
Point 2: Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine is the kind of neurotransmitter specify in learning and memory. It also enables muscle action. Jackie is a healthy person whose body releases several types of neurotransmitter especially ACh, that would help her control her muscle and make a dramatic performance. In addition, she is likely to have a good memory with the benefit of ACh, which will help her better remember the lines and learn quickly in her school play.
Teacher's feedback:
此题考查Ach的功能(muscle action/learning /memory),选择1-2种功能均可得分,但是需要结合题目举例进一步解释说明。
Point 3: Kinesthetic sense
Kinesthetic sense gives us the position and orientation of specific body parts. During repeated practice, the receptors in Jackie’s muscles send to her brain. The information, combined with visual feedback, lets Jackie keep track of her body. She can use more
precise movements and her muscles move together when she perform in a school play.
Teacher's feedback:
Kinesthetic sense和Vestibular sense都是body position senses.前者是动觉,后者是静觉。前者负责反映身体各个部分的位置、运动以及肌肉的收缩,帮助人们更好的协调动作,完成复杂的运动技能,后者负责帮助人们实现身体的平衡。
Point 4: Selective attention
Through selective attention , your awareness focuses on a particular stimulus.When Jackie is practicing, many outside stimulus such as the sound of some noisy outside the room are irrelevant to her. However,she focuses on her performance.
Teacher's feedback:
本题非常简单,考察择性注意如何帮助人们集中注意力,高效工作。
PART B
Point 5: Proactive interference
Older information learned previously interferes with the recall of information learned more recently. If Jackie used to participate in other plays, memory of her previous roles may cause a difficulty in performing this latest one.
Teacher's feedback:
1.遗忘的原因有衰退说和干扰说两种,此处考察的是干扰说。人们认为遗忘是因为学习和回忆之间受到其他刺激的干扰。
2.Proactive interference与Retroactive interference是两种干扰的形式,比较容易理解,但也很容易混淆,大家可以根据词根Pro和Re理解性记忆,历年曾多次考察过原题。
Point 6: Yerkes–Dodson law of arousal
The Yerkes–Dodson law is a relationship between state of arousal and performance. In general, most of us perform best with an optimum level of arousal, although this varies with different activities. We might perform well at an easy task with a very high level of arousal ,but the same high level of arousal would prevent us from performing well on a difficult task. If Jackie is too nervous about the play, and she may end up doing bad in the performance.
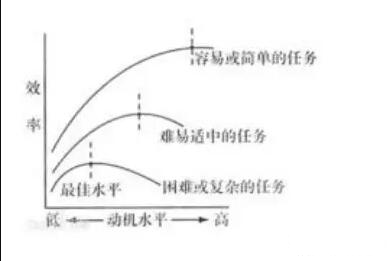
Teacher's feedback:
1.分清arousal theory 与Yerkes–Dodson law的区别。前者是动机的唤醒理论,强调人类行为的动机是因为追求最佳唤醒水平(这里可以是一种生理激活状态,即适度的焦虑)。后者是基于动机唤醒理论下细分出的定律,强调动机的最佳唤醒水平与工作任务难度有关。
2.Yerkes–Dodson law是倒U型曲线,强调中等刺激强度的动机有利于任务的完成。
3.倒U型曲线的横坐标可以是motivation/arousal level/anxiety等,都代表生理唤醒水平,只是在不同情境下叫法不同,纵坐标可以是performance/worked efficiency。
Point 7: External locus of control
A person with external locus of control tends to attribute their achievement to variables in the environment, such as other’s performance, society, and fate. When Jackie has an unpleasing performance during her rehearsal, external locus of control may lead her to blame other actor’s flaws instead of introspecting herself for space of improvement. She may not perform well in the end.
Teacher's feedback:
本题考察动机归因理论,比较简单,07年真题也出过原题,需要分清内控和外控型人在成败归因中的不同:内控型认为成败是个人原因造成,外控型人则认为成败是外部原因造成。由于人格类型不同,归因不同,最终对成败的理解也不同。
第二题
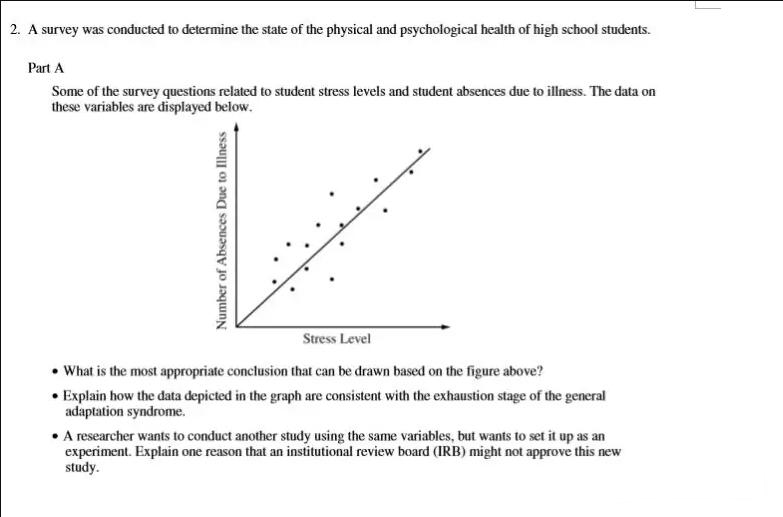

解析:本题是建立在研究方法上的常规题,题目易懂,且图表清晰,考察的相关关系,比17年第一道答题Part B的实验研究简单很多,大家可以比较一下。Part A第2题较为灵活,需要清楚GAS理论是什么,3阶段分别是怎样的过程,它给人带来的影响,并且结合图表解释。GAS在历年真题中MCQ或FRQ的出现频率极高。Part B两道题都是社会心理学的key terms,相对容易解释。Part C注意除了解释terms,最好根据实际情况结合题目举例说明。
PART A
Point 1:
The scatter plot indicates a positive correlation between Student’s absences due to illness and their stress level.
Teacher's feedback:
本题考察相关关系,非常简单。需要注意相关关系不等于无因果关系(cause and effect),相关关系的两个变量分别是由第三变量引起。
Point 2:
The exhaustion stage of GAS states that if the body is activated for too long a time, it will enter a stage of tiredness and fail to provide energy needed. A high stress level indicates the students had experienced alarm reaction and resistance stage, it make them exhausted.
So Student’s absences due to illness may a sign that indicates the body no longer has the energy to cope with continued stress in the long term.
Teacher's feedback:
GAS理论3阶段时常考到,衰竭阶段是在刺激持续存在,阻抗持续下降的情况下,适应能力的耗竭,如果有机体不休息的话会导致适应性疾病。这个理论是重中之重!
Point 3:
This particular experiment manipulating variables will bring students high stress level and illness. This is a violation of the ethical principles in psychological research because the experiment causes risk and harm to its participants.
Teacher's feedback:
此题考查心理学实验伦理道德,非常容易。
PART B
Point 4: Deindividuation
It describes the loss of self-awareness and self-restraint occurring in group situations that foster arousal and anonymity. When this phenomenon is present, the individual's sense of responsibility of behavior is obviously lost, and they may increase the risky behaviors that seem irrational or antisocial, such as fighting and brawling.
Teacher's feedback:
去个性化的原因是群体意识中身份的隐匿和责任的模糊。
Point 5: Normative social influence
Normative social influence results from a person’s desire to gain approval or avoid disapproval. People are sensitive to act some accepted and expected behavior by others.
Maybe more and more School climate encourage high school students to do risky behaviors, they conform because that social culture.
Teacher's feedback:
15年真题,无论Normative social influence和Informational social influence都是人们从众的原因,前者是因为对社会规范的遵从,后者是信息本身的价值带来的益处。
PART C
Point 6: Cognitive restructuring
Cognitive restructuring is used in cognitive therapy. It can decrease certain behaviors and adjust their thinking by making the patient realize how irrational they are. If someone can change student’s attitud of seeing their improper daily routine and bad eating habits, students may become physical healthy.
Teacher's feedback:
这道题需要对认知主义理论流派有深刻理解,并结合题目给与相应方案。
Point 7: Incentive motivation
Our behavior is not just pushed by a need, it is pulled by a desire. Incentives are some positive or negative environmental stimuluses that motivate behavior. For example , If teachers declare that anyone who have an healthy life, such as doing more exercises and eating a vegetarian diet , will get a big present or a high GPA, students will learn how to make their healthy and happy.
Teacher's feedback:
动机理论在过往真题里常考,很容易搞混,需要区分Instinct theory,drive-reduction theory,incentive therory,还有extrinstic/intrinstic motivation究竟是什么。前三个是动机理论,后一个是动机的分类形式。Instinct强调本能需要, drive-reduction强调驱力促使(个体由于生理需求未能得到满足后会产生紧张或不平衡状态,驱力是为了消除这种紧张,使得有机体平衡)。这些都属于内在动力,而incentive是外在环境的引发。它是驱力降低理论的补充,认为能满足个体需要的刺激物(无论好坏),也是诱发个体朝向目标的作用。
最新2025QS世界大学排名TOP100及国内上榜院校完整榜单
北京时间2024年6月5日凌晨,2025年度QS世界大学排名正式发布,为关注2024年高考和留学动...